Noise 噪点
Introduction
引言
"Biased" renderers allow users to specify the quality ('num samples') of effects such as glossy reflections, brute-force GI, AO and so on. This level of control is both a strength and weakness of biased rendering.
“有偏见的”渲染器允许用户指定效果的质量(‘ num samples’) ,比如光滑的反射、蛮力的 GI、 AO 等等。这种级别的控制是偏向渲染的优势和劣势。
It's a strength, because the human eye is much better at determining if a particular object/material/light is more visually important and can afford more computational effort (more samples) to get it to look clean. For this reason, proper adjustment of the various 'num samples' parameters can produce cleaner results in less time than on renderers that don't allow that level of control.
这是一种优势,因为人类的眼睛更善于判断一个特定的物体/材料/光线是否在视觉上更重要,并且能够提供更多的计算工作(更多的样本)来使它看起来更干净。由于这个原因,适当调整各种“数量样本”参数可以产生更干净的结果在更短的时间比渲染器,不允许这种水平的控制。
However, that level of control is also a weakness because the artist has to spend time tweaking the 'num samples' settings. Even worse, sometimes users may increase the 'num samples' of the wrong effect which can make rendering longer while not providing any visual benefit.
然而,这种控制水平也是一个弱点,因为艺术家必须花时间调整’数量样本’设置。更糟糕的是,有时用户可能会增加错误效果的“数量样本”,这会使渲染时间更长而不提供任何视觉效果。
For this reason, it's important to understand the different possible types of noise that exist in Redshift and know which settings to tweak to produce clean results.
因此,了解红移中可能存在的不同类型的噪声,并知道哪些设置可以调整以产生干净的结果,这一点很重要。
The different types of noise
不同类型的噪音
Any computer graphics effect that requires the shooting of multiple rays ('samples') is prone to noise.
任何需要拍摄多重射线的计算机图形学效应(‘采样’)都容易产生噪音。
These effects are the following:
这些影响如下:
- Area lighting (shadows) 区域照明(阴影)
- Ambient occlusion 环境闭塞
- Glossy reflection and refraction 光滑的反射和折射
- Brute-force GI 蛮力 GI
To improve noise on individual lights, you need to increase the "num samples" area lighting parameters of the light responsible for the noise. Typically, the larger the area light, the more samples it will need to produce clean shadows. But size is not the only concern: a light might be small but casting long, soft shadows. In this case, it also needs more samples. Generally speaking, lights producing large shadow penumbras might need 128-256 samples or even more.
为了改善单个灯的噪声,需要增加“数量样本”面积照明参数的灯负责噪声。通常情况下,面积越大的光线,它将需要更多的样本,以产生清洁的阴影。但是大小并不是唯一的问题: 光线可能很小,但是会投射出长而柔和的阴影。在这种情况下,还需要更多的样本。一般来说,产生大阴影半影的光源可能需要128-256个样本,甚至更多。
To improve noise on ambient occlusion, you need to increase the "num samples" of the AO shader node, per-material. The AO feature of the architectural shader also has a "num samples" parameter. The stronger the AO effect is (based on distance, spread, etc) the more samples it needs. 64-128 samples are often sufficient to get clean results.
为了改善环境遮挡的噪音,您需要增加 AO 着色器节点的“数量样本”,每个材质。建筑着色器的 AO 特性也有一个“ num samples”参数。AO 效应越强(基于距离,传播等) ,它需要的样本就越多。64-128个样本通常足以得到干净的结果。
To improve noise on glossy reflections/refractions, you'll need to increase the appropriate 'num samples' of the shader node, per-material. Typically, the lower the glossiness (i.e. the softer the reflection/refraction), the more samples you'll need. Also if the environment contains very bright lights and reflections, you might also need higher 'num samples' too. Low-gloss, high-contrast scenes might require large values such as 256 or even 512.
为了改善光滑反射/折射的噪点,你需要增加着色器节点的适当“数量样本”,每个材质。通常,光泽度越低(即反射/折射越柔和) ,你需要的样品就越多。此外,如果环境包含非常明亮的灯光和反射,你可能也需要更高的’数量样本’。低光泽,高对比度的场景可能需要大的值,如256甚至512。
To improve noise on Brute-force GI, you need to increase 'num rays' of the GI settings. Please refer to the brute-force GI documentation for more information on this.
为了改善噪音蛮力 GI,你需要增加 GI 设置的数目射线。有关这方面的更多信息,请参考蛮力 GI 文档。
A few examples
举几个例子
The advice of 'increase num samples when you see noise' is not very useful if you cannot tell which effect is responsible for that noise. While this typically comes with experience, we'll attempt to visually demonstrate the different types of noise so you have some idea what to expect.
如果你不知道是哪种效应导致了噪音,那么“当你看到噪音时增加数量样本”的建议就不是很有用了。虽然这通常是随着经验而来的,但我们将尝试以视觉的方式演示不同类型的噪音,这样你就有了一些期待的东西。
While adjusting 'num samples' of various effects it is recommended that you use low, fixed rate unified sampling. Set unified sampling's min/max samples to a value like 16. Please read the 'unified sampling' documentation for more details.
在调整各种效应的“样本数量”时,建议使用低、固定抽样率的统一抽样。将统一抽样的最小/最大抽样值设置为16。详情请阅读“统一抽样”文档。
Area lighting and glossy reflections
区域照明和光泽反射
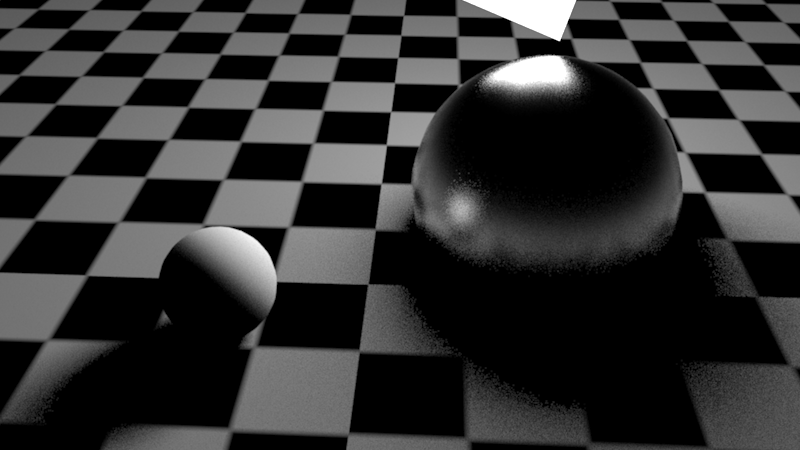
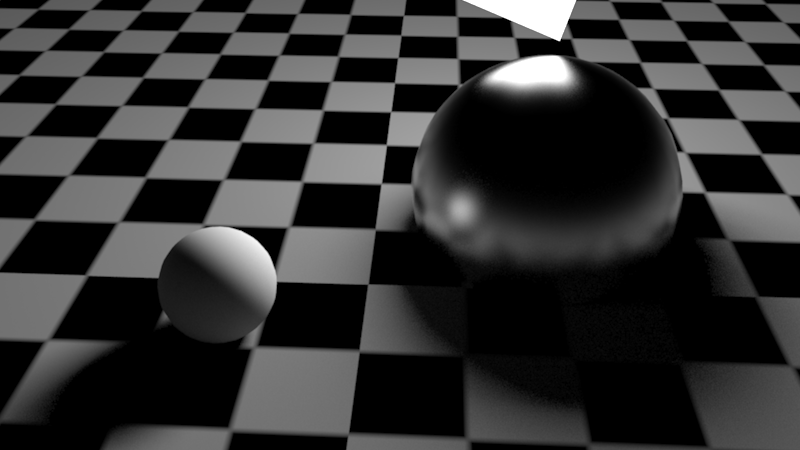
The scene shown below demonstrates area lighting and glossy reflections. The left sphere is purely diffuse while the right sphere is purely reflective. GI is disabled. The scene is using default settings. The default area light samples are 16 and default glossy reflection samples are 8. As it can be seen, these default settings are not enough to obtain a clean result.
下面显示的场景展示了区域照明和光滑的反射。左边的球体是纯粹的漫反射,而右边的球体是纯粹的反射。GI 是无效的。场景使用默认设置。默认区域光采样为16,默认光面反射采样为8。可以看到,这些默认设置不足以获得干净的结果。
Default settings for area lighting and glossy reflections produce noisy shadows and reflections
区域照明和光滑反射的默认设置会产生嘈杂的阴影和反射
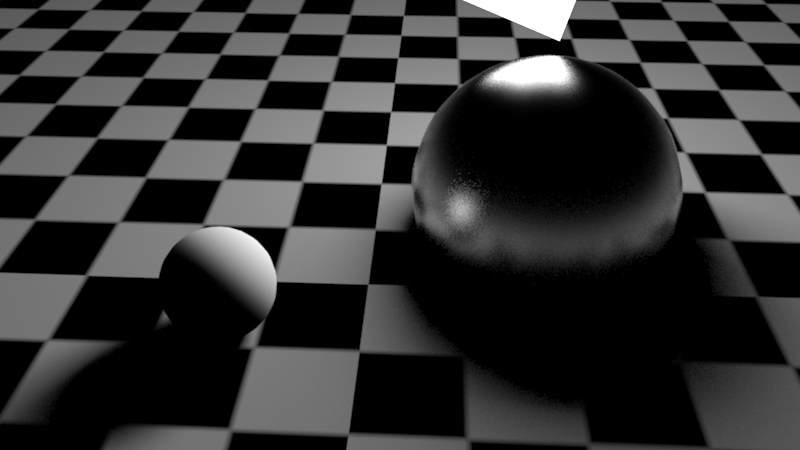
Increasing area light samples to 128 (from the default 16) improves the shadow quality and certain parts of the light reflection
增加面积光采样到128(从默认的16)提高阴影质量和光反射的某些部分
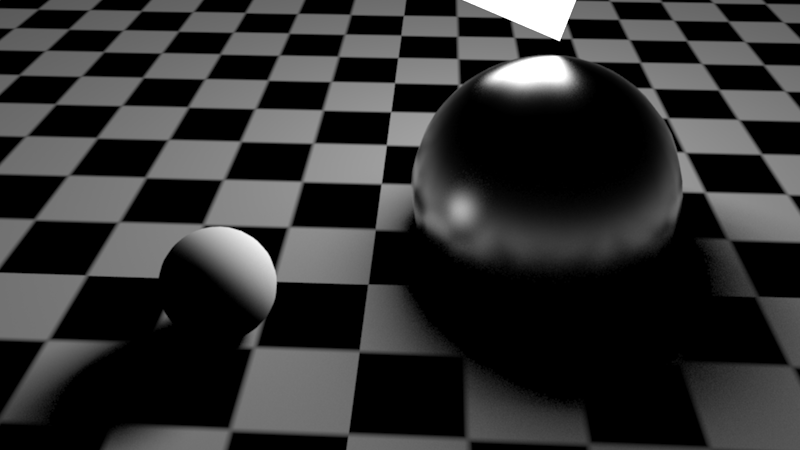
Increasing the material's glossy reflection to 256 samples improves the reflection quality
将材料的光滑反射增加到256个样品可以提高反射质量
Brute-Force GI noise
蛮力 GI 噪音
You will typically see brute-force GI noise on the parts of the scene that is not directly 'seen' by lights, such as the dark sides of objects.
你通常会在场景中不能被灯光直接“看到”的部分看到暴力的 GI 噪音,比如物体的黑暗面。
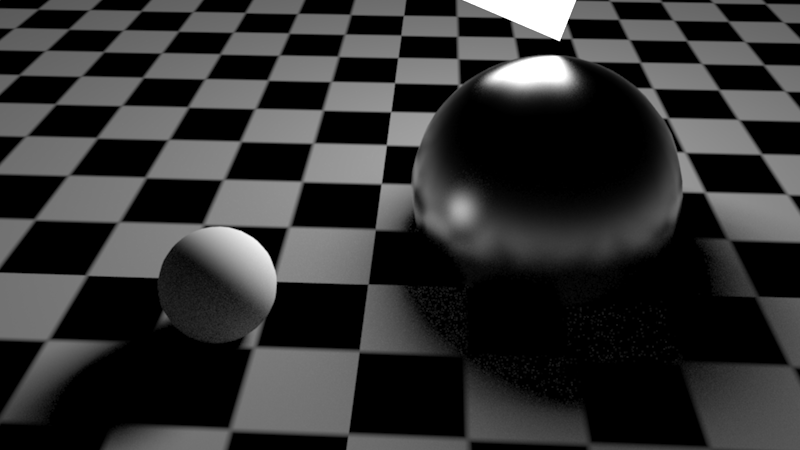
If brute-force GI is enabled for our test scene, the default setting (16 rays) produces noise underneath the diffuse sphere.
如果为我们的测试场景启用蛮力 GI,默认设置(16条射线)将在漫反射球下产生噪音。
Default brute-force GI (16 rays). There is noise underneath the diffuse sphere.
默认蛮力 GI (16条射线)。在漫反射球下面有噪音。
Increasing brute-force GI rays to 256 (from 16), improves the results
增加蛮力 GI 射线到256(从16) ,改善结果
Fireflies
萤火虫
Fireflies are a type of noise that can occur when a small percentage of rays are unlucky enough to sample extremely hot light sources, when most of the rays do not. They can also occur when a rough surface reflects or refracts an extremely hot source and there are just not enough rays to get a smooth result. Cranking up the number of rays to get a smoother result may help, but for low gloss reflections/refractions the results may actually appear worse, because the probability of the rays hitting the extremely hot source will have increased. You may find you need many thousands of rays to get a smooth result, which can dramatically impact performance.
萤火虫是一种噪音,当一小部分射线不幸采集到极热的光源时,就会发生这种噪音,而大多数射线不会采集到这种光源。当一个粗糙的表面反射或折射一个非常热的光源,并且没有足够的光线得到一个光滑的结果时,它们也会发生。调大光线数量以获得更平滑的效果可能会有所帮助,但对于低光泽的反射/折射效果实际上可能会显得更糟,因为光线击中极热光源的概率会增加。你可能会发现你需要成千上万的射线才能得到一个平滑的结果,这会极大地影响性能。
Thankfully, there are a couple of fairly cheap solutions available to help solve this problem.
值得庆幸的是,有几个相当便宜的解决方案可以帮助解决这个问题。
Max Secondary Ray Intensity 最大次级射线强度
This technique, while not physically correct, is the most effective at reducing firefly noise and requires no set up time. It works by limiting the brightness of secondary ray samples (reflection/refraction/GI), i.e. the results of lighting and reflections/refractions when seen through secondary rays. By limiting the brightness, fewer rays are needed before they average out to give a smooth result.
这项技术虽然在物理上不正确,但却是减少萤火虫噪音最有效的方法,而且不需要设定时间。它的工作原理是限制二次射线样品(反射/折射/GI)的亮度,即通过二次射线观察到的照明和反射/折射的结果。通过限制亮度,在平均之前需要较少的光线才能得到平滑的结果。
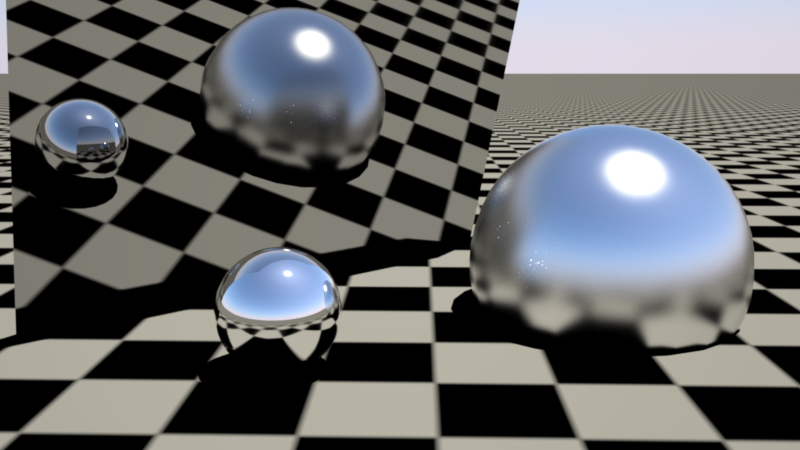
The two examples below show the same scene as above, but with a hot sun light and a mirror to demonstrate any changes in reflections.
下面的两个例子展示了与上面相同的场景,但是用一个炽热的太阳光和一面镜子来展示反射中的任何变化。
White dots ('fireflies') can be seen on the larger lower-gloss sphere. These come from the bright sun reflections on the small high-gloss sphere.
在较大的低光泽球体上可以看到白点(“萤火虫”)。这些来自于明亮的阳光反射在小高光球上。
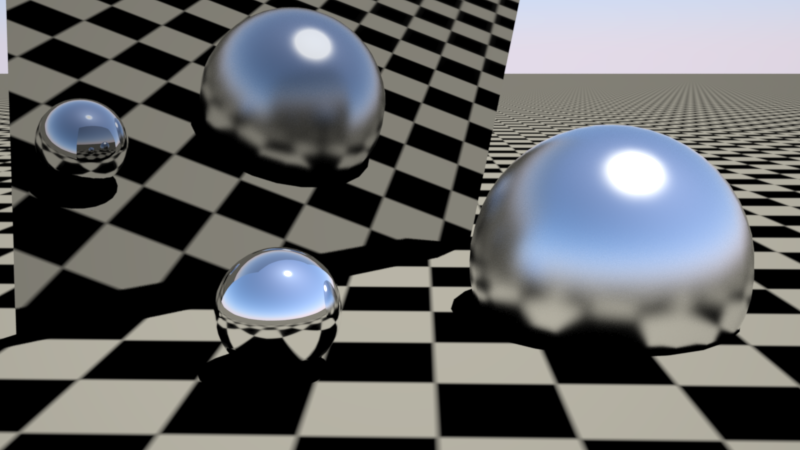
'Max Secondary Ray Intensity' used, with a value of 1.0. The white dots in the low-gloss sphere disappear, but there is some visible energy loss in the reflections as seen in the large mirror.
使用了最大次级射线强度,值为1.0。低光球面上的白点消失了,但在大镜面的反射中有一些可见的能量损失。
Lower values for 'Max Secondary Ray Intensity' do a better job of mitigating fireflies, but result in more energy loss.
较低的“最大次级射线强度”可以更好地减轻萤火虫的影响,但会导致更多的能量损失。
The 'Max Secondary Ray Intensity' value works in conjunction with Redshift's photographic exposure 'allowed overexposure' setting. An aggressive 'allowed overexposure' value (such as 0.0) means that low values (such as 1.0) should be used for 'Max Secondary Ray Intensity', otherwise you will still get fireflies! If you need to preserve high intensities on your highlights, you should avoid very low 'allowed overexposure' values (e.g. below 0.2), which in turns allows for higher 'Max Secondary Ray Intensity' values such as 2.0, 3.0 or higher to be used.
最大次级光线强度值与红移的摄影曝光“允许过曝”设置配合使用。一个积极的“允许过曝”值(如0.0)意味着低值(如1.0)应该用于“最大次级射线强度”,否则你仍然会得到萤火虫!如果你需要在你的高光部分保持高强度,你应该避免非常低的“允许过度曝光”值(例如低于0.2) ,这反过来允许使用更高的“最大次级光线强度”值,例如2.0、3.0或更高。
Ray Switch Shader 射线开关着色器
The ray switch shader can be used to change the appearance of an object through reflections/refractions, by allowing you to define a different material for different ray types. By simply cloning the shader graph for the material and toning down the reflection strength, you can reduce fireflies. While this is a more manual process, it usually results in even greater energy loss compared to using 'Max Secondary Ray Intensity' since the overall reflection intensity is being reduced, whereas 'Max Secondary Ray Intensity' is simply clamping individual secondary rays which are above a certain intensity.
通过允许你为不同的光线类型定义不同的材质,光线开关着色器可以通过反射/折射改变物体的外观。通过简单地克隆材质的着色图并调节反射强度,你可以减少萤火虫。虽然这是一个更加手动的过程,它通常会导致更大的能量损失比使用最大次级射线强度相比,因为总体反射强度正在减少,而最大次级射线强度只是夹住单个次级射线的一定强度以上。
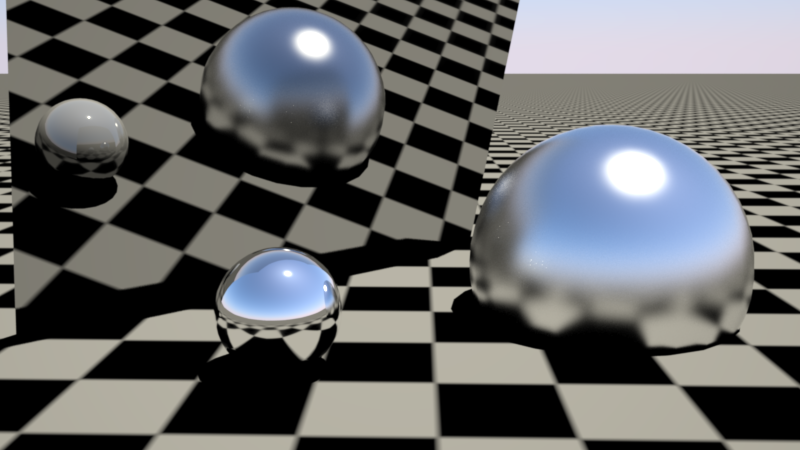
In the example below, the small sphere which was causing the fireflies in the fuzzy, larger sphere has a ray switch shader applied to it, with the reflection component manually toned down to reduce the brightness of the specular sun reflections. While this has effectively cut the fireflies from the fuzzy sphere, the consequence of the toned down reflection are very visible in the large mirror.
在下面的例子中,导致萤火虫出现在模糊的大球体中的小球体有一个光线开关着色器,反射部分手动调低以减少高光反射的亮度。虽然这样做有效地将萤火虫从模糊的球体中隔离开来,但在大镜子中,色调调低的反射效果非常明显。
Fixing fireflies using a ray switch. Fireflies are fixed (mostly) but the small sphere looks dimmer on all reflections (including the mirror plane)
用射线开关固定萤火虫。萤火虫是固定的(大部分) ,但是小球体在所有的反射(包括镜面)上看起来更暗

赶快留个言打破零评论!~