GLOSSY MATERIAL
As we mentioned in the BRDF section, there were no requirements to produce a physical accuracy reflection in the original BRDF of Octane. So when using Glossy material you can now use physical BRDFs Beckmann, GGX and Ward. With these models you can now create real surface properties such as the physical precision of the specular lobes, the fresnel effect, the law of conservation of energy, and anisotropy. As we will see in the future, you can create extremely realistic reflective surfaces with the "Metal Material" feature, which allows you to use complex refraction values that only show metallic features.
Glossy material is used to create materials with reflective properties. In reflection law, when the photon is hit by a surface, the reflection angle of light is equal to the angle of incidence. Photons do not spread around the surface as it is in the diffuse reflection. These surfaces are metal, plastic, and so on.
The energy of the irradiance from any point (I) to the point (x) on a smooth surface is reflected from this point in a special direction called the specular direction (see below diagram).
光泽材质
正如我们在BRDF部分中提到的那样,在原始的Octane BRDF中没有要求产生物理精度反射。因此,使用光泽材质时,您现在可以使用物理BRDF,贝克曼,GGX和Ward。使用这些模型,您现在可以创建真实的表面属性,例如镜面波瓣的物理精度,菲涅耳效应,能量守恒定律和各向异性。正如我们将来所看到的,您可以使用“金属材质”功能创建极其逼真的反射表面,使您可以使用仅显示金属特征的复杂折射值。
有光泽的材质用于创建具有反射特性的材质。根据反射定律,当光子被表面撞击时,光的反射角等于入射角。光子不会像在漫反射中那样在表面周围漫射。这些表面是金属,塑料等。
从任意点(I)到光滑表面上的点(x)的辐照能量都从该点沿称为镜面方向的特殊方向反射(请参见下图)。
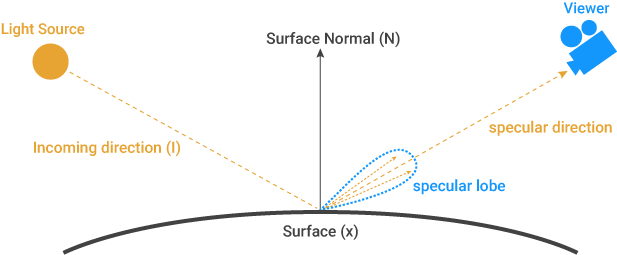
The radiance energy that comes to the surface usually reflects the light by creating a light lobe around the specular direction (Also called "specular lobe"). The shape of this lobe is determined by the difference between the exit angle of the light and the specular direction. These Specular Lobes can grow and shrink depending on the roughness value on the surface.
Reflection (actually Specular Reflection) is an important topic in CGI. Years ago we were dealing with reflection forms that were not physically correct (eg Phong BRDF). At that time, there were BRDFs, such as the Cook-Torrence or the Beckmann-Spizzichino, which had already been described but they wanted a computational power that exceeded that of their computers at that time. Now our computers are speeding up to calculate these models. But in response to this speed, we have to prepare materials by a good observation and knowledge without haste. Because entering an immediate value and expecting a realistic output often results in frustration. We repeat: Read and practice. There is no other way.
Now let's look at Octane's Glossy material options. We will not explain the parameters that we have already explained in Diffuse section and which most of the common material uses. When you select Glossy, some new parameters will appear. We will only explain these new parameters. Diffuse and Roughness parameters are important in creating Glossy Material, so we will include both of these explanations.
到达表面的辐射能通常通过在镜面反射方向周围创建光波瓣(也称为“镜面波瓣”)来反射光。该波瓣的形状由光的出射角和镜面方向之间的差确定。这些镜面波瓣会根据表面的粗糙度值而增长和收缩。
反射(实际上是镜面反射)是CGI中的重要主题。几年前,我们处理的是物理上不正确的反射形式(例如Phong BRDF)。当时,已经有BRDF,例如Cook-Torrence或Beckmann-Spizzichino,但他们希望其计算能力超过当时的计算机。现在,我们的计算机正在加快计算这些模型的速度。但是,为了适应这种速度,我们必须通过良好的观察和知识来准备材质,而不能仓促行事。因为输入立即值并期望获得现实的输出通常会导致挫败感。我们重复:阅读和练习。没有别的办法了。
现在,让我们看一下Octane的光面材质选项。我们将不解释在“漫反射”部分已经说明的参数以及大多数常用材质使用的参数。当选择光泽时,将出现一些新参数。我们将仅解释这些新参数。漫反射和粗糙度参数对于创建光泽材质很重要,因此我们将同时包括这两种说明。
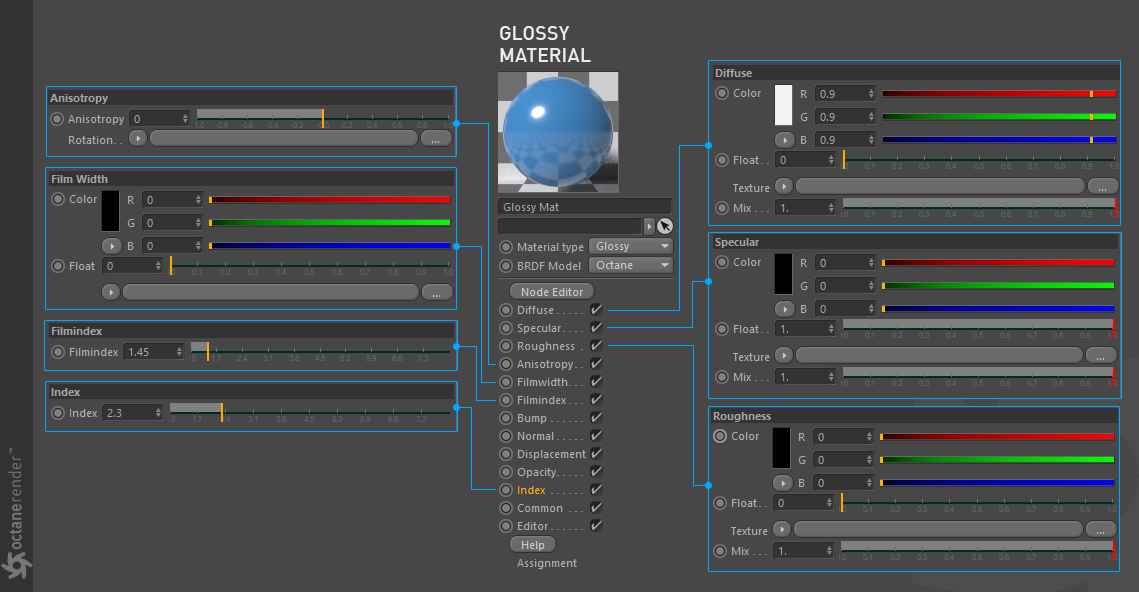
DIFFUSE
The Diffuse parameter gives the material its color. In computer graphics terminology this is also referred to as “Base Color” or “Albedo”. Diffuse color can be set using a value or by using a procedural or image based texture. But you should be careful to use diffuse in conjunction with specular color on metal-like surfaces. We will explain this in more detail in the Specular option.
漫射
漫反射参数为材质赋予其颜色。在计算机图形学术语中,这也称为“基础色”或“反照率”。漫反射颜色可以使用一个值或基于过程或基于图像的纹理来设置。但是,您应谨慎使用在类似金属的表面上将漫反射与镜面反射色结合使用。我们将在“镜面反射”选项中对此进行更详细的说明。
SPECULAR
From this parameter you can adjust the amount of reflection on the surface. We have already explained the options here in Diffuse material section. Float value is disabled when using RGB color. And vice versa. For example, if you are creating a metal surface, it is recommended that you make RGB values almost the same as diffuse color, because in the real world, the specular highlight colors of metallic surfaces are colorful. This is due to the characteristic of metals called "Conductor". Metals transmit heat and electricity well. Because of this, it is called "Conductor". They absorb different wavelenghts of the light and the color of the reflected light is the Specular Highlight. Therefore, the color of the metal material is also due to this reflected light. Gold metal, for example, appears specularly yellow as it absorbs the blue wave of visible light.
On surfaces called dielectric, there is an opposite situation, they can not transmit heat and electricity well, and when light hits these surfaces, most of the light wavelenght is not absorbed. For example, surfaces such as plastic are in the Dielectric category. If you are creating a plastic material, you can use the float parameter instead of RGB for the specular color. Thus your specular highlight will be determined according to the color of the light (mostly white).
All of this is a small recommendation if you want to make realistic material. For things like the Mograph, you can enter pretty eye-catching values. You can even use diffuse color for metallic surfaces. However, it is important to know that you should use diffuse color very lightly on reflective surfaces such as metals for a realistic result.
In the picture below, there are renders in various Specular values with a Roughness value of 0.
反射
通过此参数,您可以调整表面上的反射量。我们已经在“漫反射材质”部分中说明了这些选项。使用RGB颜色时,浮点值被禁用。反之亦然。例如,如果要创建金属表面,建议您使RGB值几乎与漫反射颜色相同,因为在现实世界中,金属表面的镜面高光颜色是彩色的。这是由于称为“导体”的金属的特性。金属很好地传递热量和电能。因此,它被称为“导体”。它们吸收不同波长的光,反射光的颜色为镜面高光。因此,金属材质的颜色也归因于该反射光。例如,金金属由于吸收了可见光的蓝色波而呈镜面黄色。在称为电介质的表面上,存在相反的情况,它们不能很好地传输热量和电流,并且当光入射到这些表面时,大部分的光波长都不会被吸收。例如,诸如塑料的表面属于“电介质”类别。如果要创建塑料材质,则可以将float参数而不是RGB用作镜面反射颜色。因此,您的镜面反射高光将根据光线的颜色(主要是白色)确定。
如果您想制作逼真的材质,所有这些都是一个小的建议。对于Mograph之类的东西,您可以输入引人注目的值。您甚至可以对金属表面使用漫反射颜色。但是,重要的是要知道,您应该在反射性表面(例如金属)上非常轻微地使用漫反射颜色,以获得真实的结果。
在下面的图片中,存在各种“镜面反射”值的渲染,“粗糙度”值为0。

ROUGHNESS
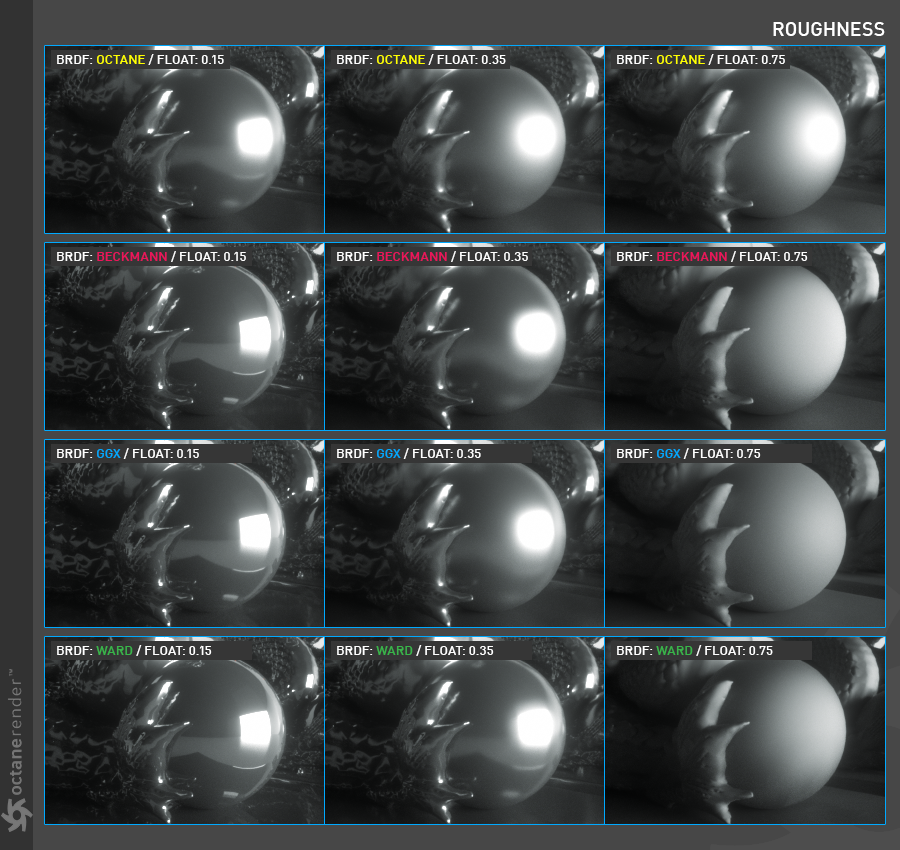
Perhaps the most important parameter of glossy material is roughness. It is a parameter that must be used absolutely for materials with reflective characteristics. This is the practical counterpart of the "microfacet" theory that we briefly describe in the BRDF section. Roughness controls the amount of specular reflection scattered on the surface. In the real world, all surfaces are rough. Even the mirror that appears as the smoothest surface is rough when viewed very closely. Here the Microfacet theory is developed on this real phenomenon. If you are wondering how the surfaces look so closely, you can look at images taken by electron microscopy (search google). You will be surprised.
Specular surfaces usually reflect light by creating a light lobe around the specular reflection direction. The shape of this lobe is determined by the difference between the exit angle of the light and the specular direction. This resulting lobe creates blurring effect due to its roughness. The larger the specular lobes, the more blur and the surface looks darker. In computer terminology, this is called "reflection blur". This value behaves in accordance with the law of conservation of energy in BRDFs that provide physical results. In other words, the incoming light is scattered in more directions during reflection, resulting in energy loss. This is the explanation that Lob goes towards darkness as the size increases. Even at extreme values, the surface almost starts to show diffuse properties (see the picture below. The other 3 brdf except the octane show this feature).
With this parameter you can also use the options we mentioned in the Diffuse section. Do not forget that not RGB but Greyscale values are important. So you must enter Greyscale values when using RGB. Or you can use Float value. You can also get very creative results with texture use.
In Octane's new BRDF models, the roughness parameter now produces more realistic results. You can see the roughness values according to different BRDF models in the picture below.
粗糙度
光泽材质最重要的参数可能是粗糙度。该参数必须绝对用于具有反射特性的材质。这与我们在BRDF部分中简要介绍的“微面”理论相对应。粗糙度控制散射在表面上的镜面反射的数量。在现实世界中,所有表面都是粗糙的。当仔细观察时,即使是最光滑的表面反射镜也很粗糙。在这里,微面理论是基于这种真实现象而发展的。如果您想知道表面如何紧密贴合,可以查看电子显微镜拍摄的图像(搜索Google)。您会感到惊讶。镜面表面通常通过在镜面反射方向周围创建光瓣来反射光。该波瓣的形状由光的出射角和镜面方向之间的差确定。由于其粗糙度,该最终的波瓣产生模糊效果。镜面波瓣越大,模糊越多,表面看起来越暗。在计算机术语中,这称为“反射模糊”。此值的行为符合提供物理结果的BRDF中的能量守恒定律。换句话说,入射光在反射期间会向更多方向散射,从而导致能量损失。这就是Lob随着尺寸增加而趋向黑暗的解释。即使在极值下,该表面几乎也开始显示出漫反射特性(请参见下图。除Octane以外的其他3个brdf都具有此功能)。
通过此参数,您还可以使用我们在“漫反射”部分中提到的选项。不要忘记不是RGB,而是灰度值很重要。因此,使用RGB时必须输入灰度值。或者,您可以使用浮点值。您也可以通过使用纹理获得非常有创意的结果。
在Octane的新BRDF模型中,粗糙度参数现在可以产生更逼真的结果。您可以在下图中看到根据不同BRDF型号的粗糙度值。
ANISOTROPY
This parameter is present in our material arsenal as a result of the new BRDF models. The anisotropy is the reflection value changes by turning the surface around its normal. Examples of anisotropic surfaces include polished metal, human hair, fur and wood. In Octane, you can use the anisotropy feature for 3 new BRDF models. You should enter the roughness value for to use this effect. You can increase or decrease the roughness according to the BRDF model you choose. Anisotropy has several options, let's explain them.
Anisotropy: From here you can determine the amount of anisotropy you will apply to the surface. It can be a negative or positive value. Do not forget to enter a value for the roughness.
Rotation: From here you can rotate anisotropy by defining a texture. With the texture you use, you can get a wide variety of effects by turning the surface normals. You can use any texture image or procedural, provided that it's a gray scale. Even with the new OSL texture, you can create completely different results.
If you want to make a realistic anisotropy, be sure to first observe the physical properties of the material you will create. All anisotropy surfaces shows absolutely roughness / specular and IOR properties. Without this, you can not create an anisotropic surface. In particular, surfaces showing anisotropic properties such as polished metal, wood and fur show distinct microfacet features from each other. Also take a shot of the subject for reference if you have to. Finally, set your model's surface normals and UV map settings according to your objective.
The following picture shows the anisotropy properties of different BRDF models. In this image the roughness value is fixed and a gray scale image texture is used for rotation.
各向异性
由于新的BRDF模型,该参数存在于我们的材质库中。各向异性是通过围绕曲面的法线旋转反射值而引起的。各向异性表面的例子包括抛光金属,人发,毛皮和木材。在Octane中,可以将各向异性功能用于3个新的BRDF模型。您应该输入粗糙度值才能使用此效果。您可以根据选择的BRDF模型增加或减少粗糙度。各向异性有几种选择,让我们对其进行解释。各向异性:从这里可以确定要应用于曲面的各向异性的数量。它可以是负值或正值。不要忘记输入粗糙度值。
旋转:从此处可以通过定义纹理来旋转各向异性。使用您使用的纹理,可以通过旋转表面法线来获得各种效果。您可以使用任何纹理图像或程序,只要它是灰度即可。即使有了新的OSL纹理,您也可以创建完全不同的结果。
如果要实现逼真的各向异性,请务必先观察将要创建的材质的物理特性。所有的各向异性表面都显示出绝对的粗糙度/镜面反射和IOR特性。没有这个,就不能创建各向异性的曲面。尤其是,具有各向异性特性的表面(例如抛光金属,木材和毛皮)彼此之间显示出明显的微面特征。如果需要,还可以拍摄该主题以供参考。最后,根据您的目标设置模型的表面法线和UV贴图设置。
下图显示了不同BRDF模型的各向异性属性。在此图像中,粗糙度值是固定的,并且灰度图像纹理用于旋转。

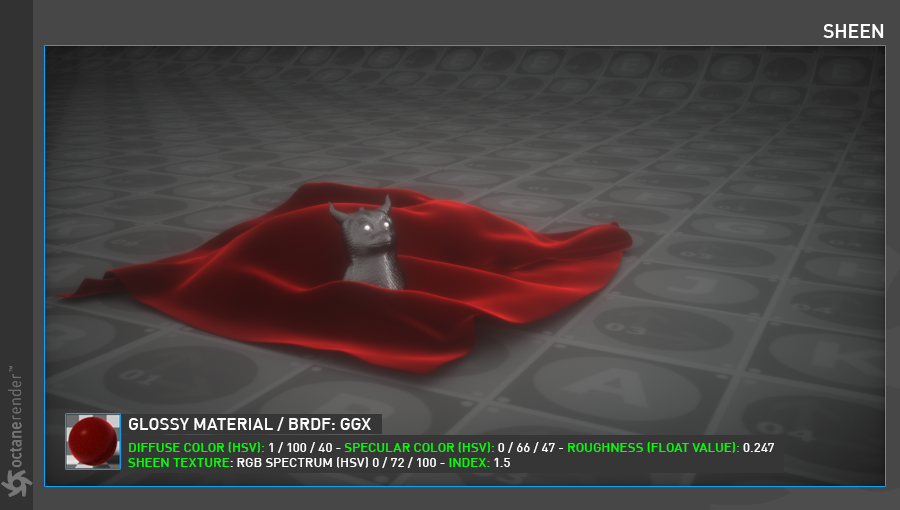
Sheen
This is mainly used for simulating clothes and velvet/satin like materials. It's basically increasing reflectance for grazing angle with varying roughness. Less roughness means a sharper peak of sheen reflection around the grazing angle, higher roughness means a less sharp peak and a more spread out sheen reflection across the fabric surface.
This feature works in new BRDF models. So choose the other BRDFs instead of the default Octane BRDF. Sheen is also a BRDF model and is written according to the formulas on this link.
To use Sheen, create a "Glossy" material and enter the values you see in the picture below to get started. The parameter that is important after completing the main material setup is the "Roughness" parameter. You can change the sheen look by playing with this parameter. It is also possible to use Sheen more efficiently with Mix material.
The Sheen feature is definitely a great addition to Octane material creation. Previously we used "Falloff" texture to make fake fabric. We no longer need this type of tricks thanks to the sheen feature.
光泽
这主要用于模拟衣服和类似天鹅绒/缎子的材质。它基本上是在改变粗糙度的情况下提高掠角的反射率。粗糙度越小,意味着在掠射角附近的光泽反射峰越尖锐;粗糙度越高,意味着在织物表面上的峰反射越尖锐度越低,且光泽分布越分散。此功能适用于新的BRDF型号。因此,请选择其他BRDF,而不是默认的Octane BRDF。 Sheen也是BRDF模型,并根据此链接上的公式编写。
要使用Sheen,请创建“光面”材质并输入下图所示的值以开始使用。完成主要材质设置后,重要的参数是“粗糙度”参数。您可以通过使用此参数来更改光泽外观。对于混合材质,也可以更有效地使用光泽。
光泽功能无疑是Octane材质创建的一项重要补充。以前我们使用“ Falloff”纹理制作假织物。有了光泽功能,我们不再需要这种技巧。
FILM WIDTH & FILM INDEX
Film width simulates the look of a thin film of material on the surface. This is useful when you want to create an effect such as the rainbow colors that appear on the surface of an oil slick. Or a soap bubble. Larger values increase the strength of the effect. The Film Index controls the Index of Refraction of the thin film, use this option to adjust the colors visible in the film. For this parameter you can also enter RGB color/Float Value and image/procedural texture values. In the picture below, a gray scale image texture is used for Film width. Film Index is 2.2.
胶片宽度和胶片索引
膜宽模拟表面上的材质薄膜的外观。 当您要创建效果(例如浮油表面上出现的彩虹色)时,此功能很有用。 或肥皂泡。 较大的值会增加效果的强度。 胶片折射率控制薄膜的折射率,使用此选项可以调整胶片中可见的颜色。 对于此参数,您还可以输入RGB颜色/浮点值和图像/程序纹理值。 在下面的图片中,灰度图像纹理用于胶片宽度。 电影索引是2.2。

INDEX (INDEX OF REFRACTION)
This parameter determines the reflection strength of the surface according to the fresnel reflection law. Also called IOR or Refractive Index. Fresnel is the surface reflection of the observed angle and the surface IOR (Index of Refraction) values. The Fresnel effect is, which reflects less light from the direct-facing surfaces than the other angles. In this case the value you enter will change the Fresnel reflection (see below picture).
in reality each surface has a refractive index. For example, if you want to enter a correct value in the index part here, be sure to use https://refractiveindex.info/ as your online resource. The "Selected data for 3D artist" section on the main drop down menu is a good start. The values that concern us here are the "n" and "k" values. These values are actually called "complex index of refraction". But there is no area in Octane where you can enter these values except "Metal Material". In this case, you can only enter "n" in the index section. The number "k" is the value of extinction coefficient. Since the index is a complex phenomenon, we will refer again to both "Specular" and "Metal Material" sections.
指数(折射指数)
此参数根据菲涅耳反射定律确定表面的反射强度。也称为IOR或折射率。菲涅耳是观察到的角度和表面IOR(折射率)值的表面反射。菲涅耳效果是,与其他角度相比,它反射的直射表面的光更少。在这种情况下,您输入的值将更改菲涅耳反射(请参见下图)。
实际上,每个表面都具有折射率。例如,如果您想在此处的索引部分中输入正确的值,请确保使用https://refractiveindex.info/作为您的在线资源。主下拉菜单上的“ 3D艺术家的选定数据”部分是一个好的开始。这里与我们有关的值为“ n”和“ k”值。这些值实际上称为“复数折射率”。但是,在“Octane”中,没有任何区域可以输入“金属材质”之外的这些值。在这种情况下,您只能在索引部分输入“ n”。数字“ k”是消光系数的值。由于索引是一个复杂的现象,因此我们将再次参考“特殊”和“金属材质”部分。










赶快留个言打破零评论!~