Metallic MATERIAL
This material type is used to create more realistic metal. Metallic Material is clearly distinguished from the Glossy material both in terms of specular and IOR. In the real world, the reflection properties of metals are very high; and as we have already mentioned, it is determined according to the characteristics of the light reflected back because it absorbs certain wavelengths of the light. So the specular highlight color is usually colorful on copper and gold metals. But where do these colors come from? Why is gold metal yellow-orange and silver white?
There is a very complicated and technical description of the situation, but we will make a short description.
金属材质
该材质类型用于创建更逼真的金属。在镜面反射和IOR方面,金属材质与光泽材质明显不同。在现实世界中,金属的反射特性非常高。正如我们已经提到的,它是根据反射回的光的特性确定的,因为它吸收特定波长的光。因此,镜面高光颜色通常在铜和金金属上是彩色的。但是这些颜色从哪里来?为什么金金属是橙黄色而银白色?
对这种情况有非常复杂的技术描述,但我们将做一个简短的描述。
When light (electromagnetic radiation) hits the surface of a metal, it gets absorbed by electrons orbiting the metal atoms, and re-emitted as the electrons fall back to a more stable configuration. The electrons are free to move throughout the metal, which explains its high electrical and heat conductor. Certain wavelengths of the rays absorbed by the metal surfaces cause energy exchange between the electrons. The configuration of these electrons differs according to the type of metal. In metals, only copper and gold show certain color in visible light. The color of gold and copper is related to its electron structure. In the case of gold, the energy difference between electrons in gold is about 400-492nm and this strong absorption cut out the blue light from the reflection, creating the yellow-orange color of gold. Copper has also similar effect for its electron structure but with lower absorption energy (Blue/Blue-Violet), thus we see orange color. For example, silver metal absorbs more or less all wavelengths of light, we see bright white color. The table below shows the colors we see after absorbing certain wavelengths.
当光(电磁辐射)撞击金属表面时,它会被围绕金属原子运行的电子吸收,并随着电子落回到更稳定的构型而重新发射。电子在整个金属中自由移动,这解释了其高电导率和热导率。金属表面吸收的某些波长的射线引起电子之间的能量交换。这些电子的构型根据金属的种类而不同。在金属中,只有铜和金在可见光下显示某些颜色。金和铜的颜色与其电子结构有关。在金的情况下,金中电子之间的能量差约为400-492nm,这种强大的吸收作用将反射光中的蓝光切断,形成了金黄色至橙色。铜的电子结构也具有类似的作用,但是吸收能量较低(蓝/蓝紫),因此我们看到橙色。例如,金属银或多或少地吸收了所有波长的光,我们看到了明亮的白色。下表显示了我们吸收某些颜色后看到的颜色

So if you want to make a realistic metal using metallic material, it is the right thing to set the right color from specular.
因此,如果要使用金属材质制作逼真的金属,则从镜面反射设置正确的颜色是正确的选择。
We also highly recommend using the new BRDF models when using metallic materials. Because the new BRDF models use much more advanced Fresnel formulas than the default Octane BRDF. As a result your render output will be much more realistic.
Now let's look at Octane's Metallic material options. We will not explain the parameters that we have already explained in Diffuse/Glossy or Specular section. When you select Metallic, some new parameters will appear. We will only explain these new parameters. Diffuse, specular, specular map and index parameters are important in creating Metallic Material, so we will include these explanations.
我们还强烈建议在使用金属材质时使用新的BRDF型号。 因为新的BRDF模型使用的菲涅耳公式比默认的Octane BRDF更高级。 结果,您的渲染输出将更加真实。
现在,让我们看一下Octane的Metallic材质选项。 我们将不解释在“漫反射/光泽”或“镜面反射”部分中已经说明的参数。 选择“金属”时,将出现一些新参数。 我们将仅解释这些新参数。 漫反射,镜面反射,镜面反射贴图和索引参数对于创建“金属材质”很重要,因此我们将包括这些说明。

DIFFUSE
This parameter does not work alone in case of metallic material but works with specular map. "Metals have their own color" and "Give color to the metal" are different things. One is the color we see reflected after the metal surface absorbs a certain wavelength of the light. This is a situation that needs to be done from the specular option or from the IOR section.
"Coloring a metal" is like painting a natural metal element. Can also called "Coating". For example, what is called "Car Paint" is actually this. If your goal is to create a metal color that does not offer physical realism but looks nice to the eye, you can use this option with specular map. For example, if you want to create a purple colored car, you can use this option. Since there is no metal variety called purple metal, you can put your imagination into action. Diffuse parameter will be explained in more detail in our specular map explanations.
漫射
在金属材质的情况下,此参数不能单独使用,但对镜面贴图有效。 “金属有自己的颜色”和“赋予金属颜色”是不同的东西。一种是在金属表面吸收一定波长的光之后我们看到的反射颜色。这种情况需要通过镜面反射选项或IOR部分来完成。
“为金属着色”就像绘画天然金属元素一样。也可以称为“涂层”。例如,所谓的“汽车油漆”实际上就是这个。如果您的目标是创建一种不提供物理逼真效果但看起来很美观的金属色,则可以将此选项与镜面贴图一起使用。例如,如果要创建紫色汽车,则可以使用此选项。由于没有称为紫色金属的金属品种,因此您可以发挥想象力。漫反射参数将在我们的高光贴图说明中更详细地说明。
SPECULAR
According to the IOR type you choose, you can set the color and amount of reflection of the metallic material using this option. You can change the reflection amount with the float value or set the both color and reflection amount with the HSV values. If you use HSV value, you can adjust the amount of reflection with "V" parameter. Thus you can also make your metal material "Dielectric" or "Conductor". There are quite enough resources on the web for these two concepts. We recommend you look.
Let's say if your goal is to make a real Gold, you will enter the color here or you will use "RGB Ior" (which you will get much more realistic results). We will explain more detailed description about the connection of IOR with specular in the "Index" section.
Info: In reality, the reflection quantities of real metals types have their own reflectance and do not change. Keep this information in mind. So if your goal is to create a full realistic metal, do not play with the reflection amount. If you do not intend to make realistic metal, you can ignore this warning
反射
根据您选择的IOR类型,您可以使用此选项设置金属材质的颜色和反射量。您可以使用float值更改反射量,或者使用HSV值设置颜色和反射量。如果使用HSV值,则可以使用“ V”参数调整反射量。因此,您也可以将金属材质制成“介电”或“导体”。网络上有足够的资源可用于这两个概念。我们建议您看看。
假设您的目标是制作真实的金色,您将在此处输入颜色,或者使用“ RGB Ior”(将获得更逼真的结果)。我们将在“索引”部分中解释有关IOR与镜面反射的连接的更详细描述。
信息:实际上,真实金属类型的反射量具有自己的反射率并且不会改变。请记住这些信息。因此,如果您的目标是创建完整逼真的金属,请不要使用反射量。如果您不打算制作逼真的金属,则可以忽略此警告

SPECULAR MAp
This parameter is used to mix the RGB and texture values of Diffuse and Specular. There are various ways to use it. If you want to input an RGB diffuse value to the metal material, you can use this parameter to see the diffuse color and also you can change the amount of reflection as mentioned above. The texture types you assign here can be greyscale / RGB or procedural. The following pictures show two different uses.
特殊映射
此参数用于混合“漫反射”和“镜面反射”的RGB和纹理值。 有多种使用方式。 如果要向金属材质输入RGB漫反射值,则可以使用此参数查看漫反射颜色,也可以如上所述更改反射量。 您在此处分配的纹理类型可以是灰度/ RGB或程序。 下图显示了两种不同的用法。


INDEX
This controls the Complex IOR settings of the metallic material. By default metals use the Schlick approximation for the Fresnel effect. For a more precise falloff, a complex IOR can be entered (commonly known as n and k values). When a complex IOR is set up, the metallic color will get scaled so the brightness matches the Fresnel falloff for that IOR.
This complex IOR is very complicated topic to explain here. Let's try to simplify the situation: The "n" and "k" are the "values", and we can say that the sum of the reflection is equal to the reflected part and the attenuation effect. The "n" value is the Index of Refraction value. "k" is a phenomenon called absorption loss (or extinction coefficient) and indicates how much light is weaken after entering a surface. The "k" value you see here points to this. In fact, "k" indicates the amount of absorption loss when the electromagnetic wave propagates through the medium. But in octane it is just for more accurate fresnel effect.
指数
这可以控制金属材质的“复杂IOR”设置。默认情况下,金属对菲涅耳效应使用Schlick近似。为了获得更精确的衰减,可以输入一个复杂的IOR(通常称为n和k值)。设置复杂的IOR时,金属色将缩放,因此亮度与该IOR的菲涅耳衰减匹配。这个复杂的IOR是一个非常复杂的主题,在这里要说明。让我们尝试简化这种情况:“ n”和“ k”是“值”,可以说反射的总和等于反射部分和衰减效果。 “ n”值是折射率值。 “ k”是一种称为吸收损耗(或消光系数)的现象,表示进入表面后减弱了多少光。您在此处看到的“ k”值指出了这一点。实际上,“ k”表示电磁波传播通过介质时的吸收损失量。但是在Octane中,这只是为了获得更精确的菲涅耳效果。
Let's explain this section in more detail:
让我们更详细地解释本节:
Metallic Reflection Mode
This changes how the reflectivity is calculated according to three types: "Artistic", "Ior + Color" and "RGB Ior".
金属反射模式
这改变了根据三种类型计算反射率的方式:“ Artistic”,“ Ior + Color”和“ RGB Ior”。
ARTISTIC
You can only use Specular color in this mode. The values you will enter into the "Index of refraction" below have no impact. It is simple and ideal for non-realistic results.
艺术的
您只能在此模式下使用镜面反射颜色。您将在下面的“折射率”中输入的值没有影响。它是简单且理想的非现实结果。

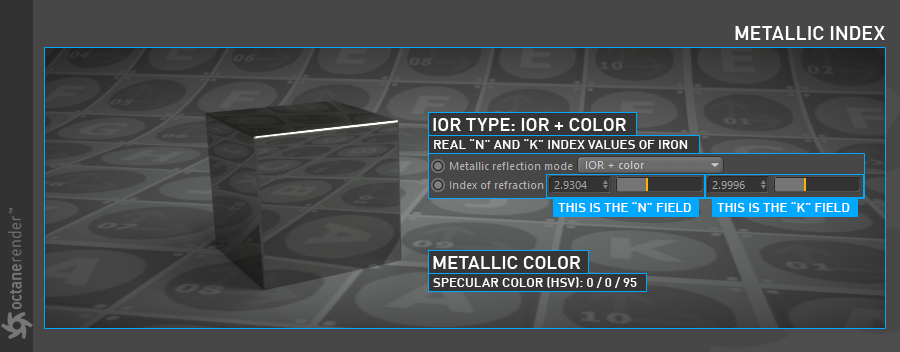
IOR + color
In this mode you can also use "n and k" IOR values as "Index of Refraction" along with the Specular color. "n" and "k" are actual index values. For these values go to refractiveindex.info site and enter real IOR values according to material types you selected. Use the numeric field for "n" on the left and "k" on the right. As it's color, you can still specify any color from specular channel.
IOR +颜色
在此模式下,您还可以将“ n和k” IOR值与“镜面反射”颜色一起用作“折射率”。 “ n”和“ k”是实际索引值。 对于这些值,请转到fractureindex.info网站并根据您选择的材质类型输入实际IOR值。 将数字字段用于左侧的“ n”和右侧的“ k”。 由于是颜色,您仍然可以从镜面反射通道中指定任何颜色。
RGB IOR
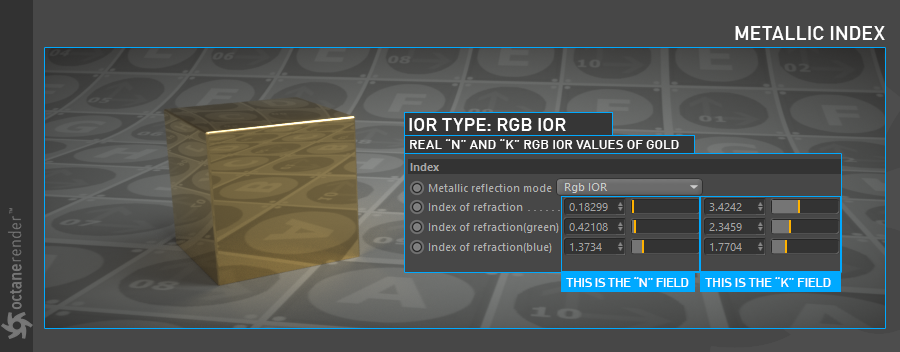
Using this mode you can get the most accurate result. Here you can apply the theory that we mentioned at the beginning in a practical sense. Using the wavelengths of the visible spectrum, you can specify both color and index (Specular use disabled). There are three main spectrum we will use for this: Red, Green and Blue. The complex IORs of each wavelength are different ("n" and "k"). As we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, it is a situation that changes according to the electron structure of materials. Take Gold, for example, and see how it works in Octane. Gold absorbs a strong absorption at 450nm wavelength. So we do not see a blue color in the gold material. At other wavelengths, absorption is not strong.
Now you can use RGB IOR with this information. For this you need to know which wavelengths for all three channels correspond to: 650nm for red, 550nm for green and 450nm for blue.
RGB IOR
使用此模式可以获得最准确的结果。 在这里,您可以在实践中应用我们在开始时提到的理论。 使用可见光谱的波长,您可以指定颜色和索引(禁止特殊使用)。 我们将使用三个主要光谱:红色,绿色和蓝色。 每个波长的复IOR不同(“ n”和“ k”)。 正如我们在本章开始提到的那样,这种情况根据材质的电子结构而变化。 以Gold为例,看看它在Octane中如何工作。 金在450nm波长处吸收强吸收。 因此,我们在金材质中看不到蓝色。 在其他波长处,吸收不强。
现在,您可以将RGB IOR与该信息一起使用。 为此,您需要知道所有三个通道对应的波长:红色为650nm,绿色为550nm,蓝色为450nm。

Now go to the site Refractiveindex.info and select "Gold" in the "selected data for 3D artist" section. Once you have chosen this, enter 0.65 (ie 650nm) for Red in the Wavelength section and use the values of "n" and "k" immediately below for the red light in the Octane Index (the first row). Do this in the other wavelengths and enter the values one by one in the respective locations. If you have done right, the realistic result of Gold metal will be as followin picture. Of course fundementally, everything else can be very different with other cosmetic factors and texture use. But that's not the point.
现在转到网站Refractiveindex.info并在“为3D艺术家选择的数据”部分中选择“黄金”。 选择此选项后,在“波长”部分中为“红色”输入0.65(即650nm),并将正下方的“ n”和“ k”值用于Octane指数(第一行)中的红光。 在其他波长下执行此操作,然后在各个位置一个一个地输入值。 如果您做对了,那么金金属的实际效果将如下图所示。 当然从根本上来说,其他所有因素都可能与其他修饰因素和纹理使用情况大不相同。 但这不是重点。










赶快留个言打破零评论!~